Themen dieses Blogartikels:
Table of contents
- What is Nattokinase?
- Kinase vs. Protease
- How does nattokinase work in the body?
- How Nattokinase affects blood coagulation
- Effect of Nattokinase on Inflammation
- Relationship between nattokinase, vascular health and cardiovascular disease
- How to take Nattokinase?
- Are there any risks or side effects when taking nattokinase?
- Conclusion on Nattokinase: A promising future
- Bibliography
Introduction
In Japan, it has long been known that nattokinase has a positive effect on well-being. In Germany, however, many people are completely unaware of the enzyme that is responsible for blood clotting, the cardiovascular system and high blood pressure. We want to change that with this article: We will introduce you to the enzyme nattokinase, tell you what nattokinase has to do with soybeans and look at studies to see what effect it has on the body.
Disclaimer: This article is not a substitute for medical advice, but provides general information. A therapy concept must be drawn up in consultation with a doctor or therapist.
What is Nattokinase?
Nattokinase is an enzyme that owes its name to the Japanese dish natto. Natto is made by cooking soybeans and fermenting them with certain bacteria, which produce nattokinase as they work. In Japan, eating natto, which incidentally also contains other good enzymes, is considered to have a positive effect on well-being and is said to be good for the body in cases of cardiovascular disease, for example.
Kinase vs. Protease
Contrary to what the name suggests, the enzyme nattokinase does not belong to the enzyme class of kinases, but to the proteases. These are responsible for breaking down proteins. Nattokinase, for example, breaks down fibrin, or more precisely the fibrin polymers that form during blood clotting. This is why nattokinase and similar enzymes are often referred to as natural blood thinners. We will look in detail in this article to see whether this is true.
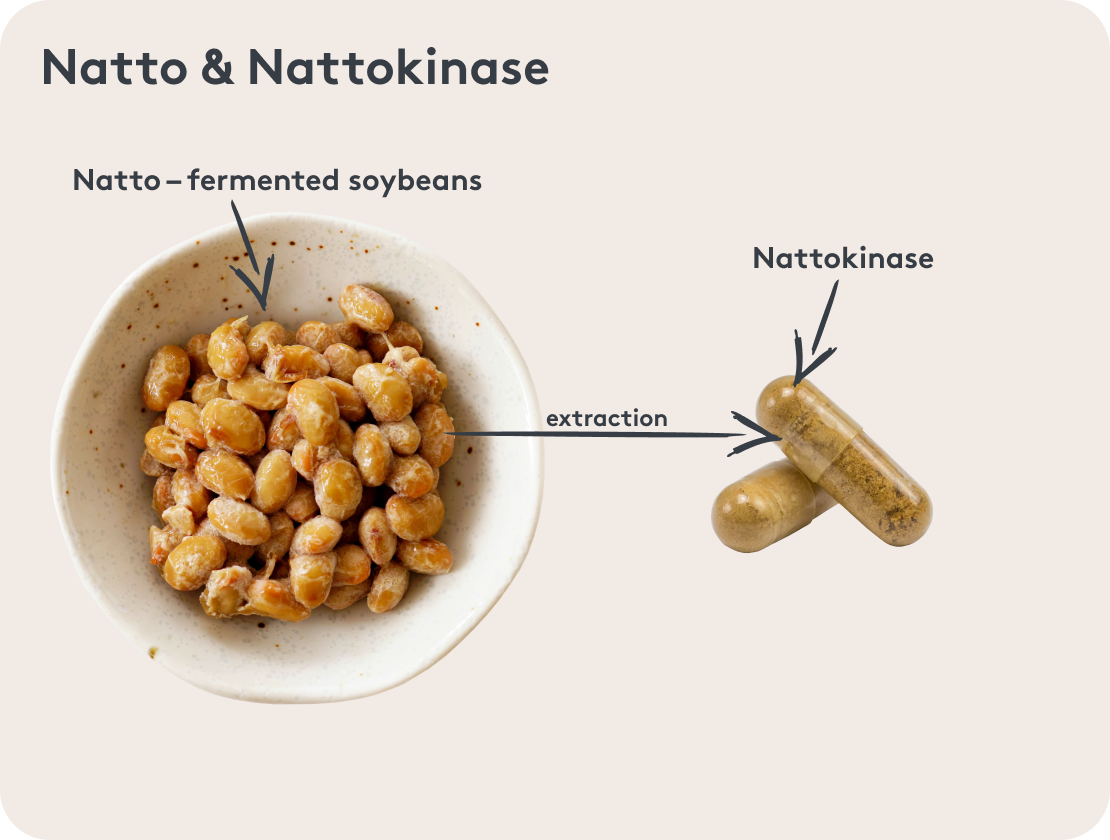

How does nattokinase work in the body?
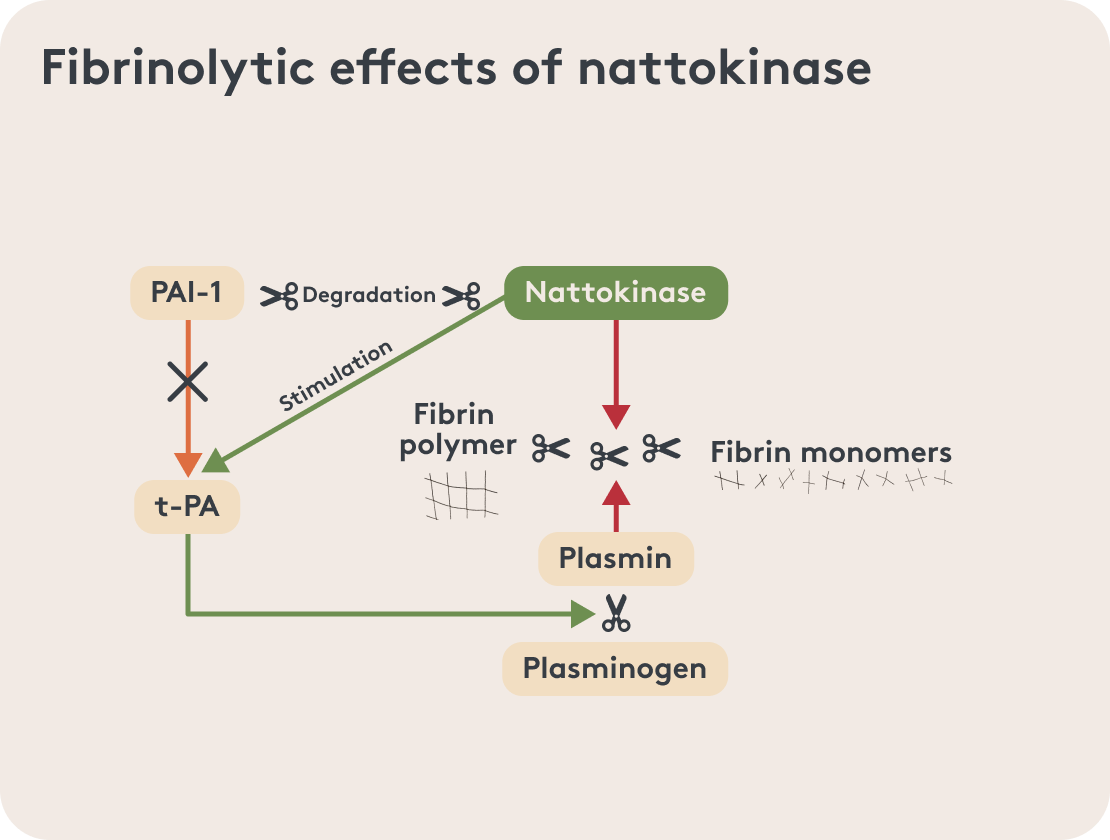
As a protease, nattokinase is specifically responsible for breaking down fibrin. It also activates the tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), which in turn breaks down plasminogen into active clot-dissolving plasmin¹. All in all, nattokinase has potential fibrinolytic and thrombolytic effects. This means that nattokinase may have the ability to dissolve blood clots and thus covers a wide range of different areas of application.

Advertisment
Plant-based nattokinase from fermented soybean extract
Combined with other plant enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD), papain & bromelain enzymes support blood clotting & the breakdown of macronutrients (thus digestion)
Vitamin C from acerola supports collagen formation for healthy blood vessels
Combined with the amino acids L-arginine & L-proline to support collagen formation for healthy blood vessels

How Nattokinase affects blood coagulation
It is obvious that nattokinase affects blood clotting because of its function. Let's take a look at what researchers have discovered in studies on blood clotting and nattokinase:
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled intervention study from 2015 in the magazine Scientific Reports showed how strong the fibrinolytic effect was after a single administration of 2,000 fibrinolytic units (FU)². The result: Even with the single dose, there was a significant increase in fibrin degradation products after about six hours , which indicate that enzymatic cleavage had occurred. In addition, the D-dimer parameter was increased after four and eight hours. The D-dimer also indicates that fibrin polymers were dissolved . Antithrombin concentrations were also significantly increased.
This result suggests a significant change after taking nattokinase, but still within the normal range. This is important to know because an abnormal change would likely be associated with a strong side effect profile. It can therefore be assumed that nattokinase causes some blood thinning, but this is within a healthy range.
Effect of Nattokinase on Inflammation
Inflammation, or chronic inflammation, plays a role in the development of many diseases. Cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis are actually caused by chronic inflammatory processes in the vascular wall.
For this reason, an in vitro and in vivo study from 2020 looked at whether and how nattokinase can influence these inflammatory processes and increased oxidative stress³. It found that the enzyme can inhibit LPS-induced inflammatory processes and thus regulate the overactivation of macrophages. Overall, it was shown that nattokinase was able to reduce oxidative stress and had anti-inflammatory effects in mice, at least in vitro and in vivo.
How this effect can be transferred to humans remains to be seen – after all, the enzyme was only discovered in 1987. Research on this topic is therefore still in its infancy.
Relationship between nattokinase, vascular health and cardiovascular disease
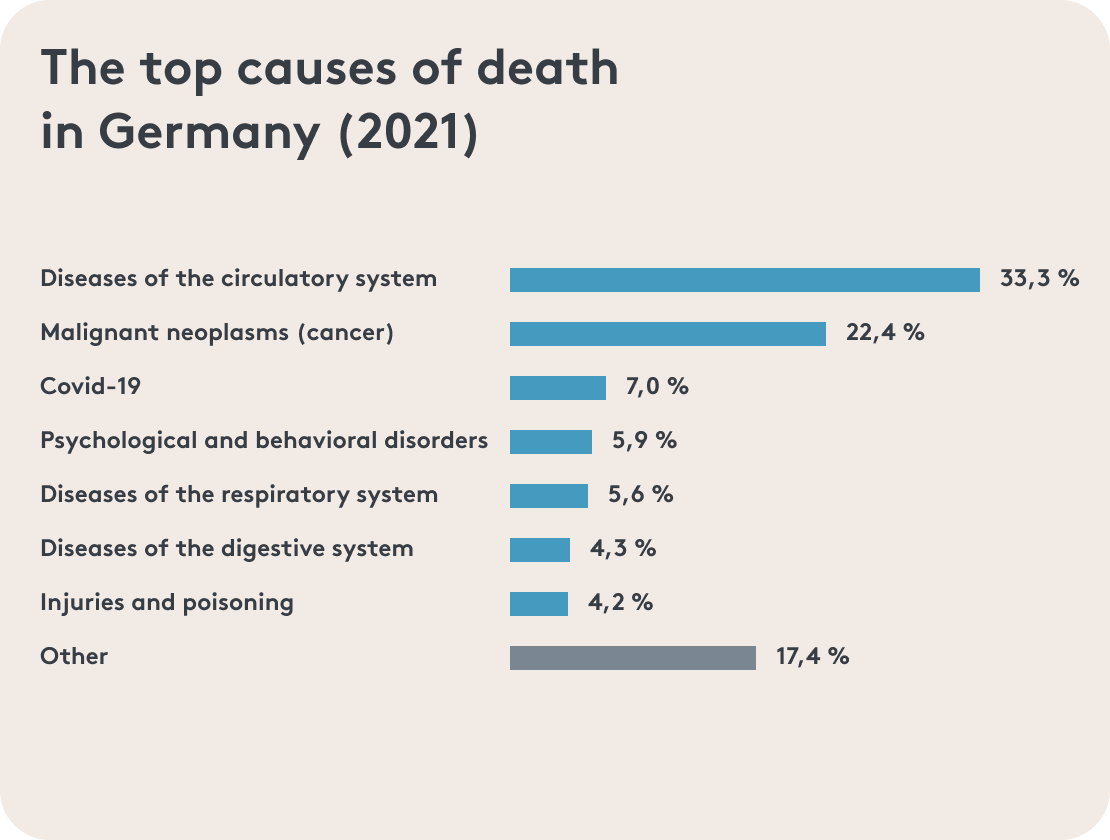
When we talk about blood clotting and chronic inflammation, the path to the cardiovascular system is not far. Did you know that cardiovascular diseases were responsible for about 27% of deaths worldwide in 2019⁴? In Germany, the figure was even slightly over 33% in 2021⁵.
It is therefore important to support the body in the fight against these diseases with as few side effects as possible and also preventively in order to reduce the cardiovascular risk. So what is the evidence regarding nattokinase and vascular health?

Let's take a look at the topic of blood pressure, which is related to cardiovascular problems. Several research groups are also working on this and are conducting studies to find out whether the fibrinolytic enzyme has an influence here.
For example, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study from 2008 showed that in patients with untreated high blood pressure or borderline high blood pressure, both systolic and diastolic blood pressure decreased⁶. The reason for this is probably at least partly the effect as an ACE inhibitor⁷. ACE, the angiotensin-converting enzyme, is a popular target of many blood pressure-lowering drugs.
Other working groups focused on the effects on blood lipid levels and atherosclerosis. For example, a large clinical study with 1,062 participants⁸ showed that after taking 10,800 FU of nattokinase for twelve months, both LDL cholesterol and triglycerides decreased significantly, while "good" HDL cholesterol increased. In addition, 683 patients were examined using ultrasound to determine whether there was an improvement in atherosclerotic changes in the carotid arteries (colloquially known as the carotid artery). The size of existing plaques and the thickness of the vessels decreased significantly, with the improvement in size being an average of 66.5% compared to before taking the drug.
Here too, nattokinase appears to have positive effects and is therefore a promising addition to therapy. Of course, we must continue to wait for research results before firm recommendations can be made and guidelines perhaps even supplemented.
Until then, however, we can at least address two other questions: What dosage of Nattokinase should you take and what side effects are there?
How to take Nattokinase?
The enzyme nattokinase is found in fermented natto or can be consumed as a dietary supplement in the form of capsules. Nattokinase capsules usually contain an amount of enzyme with an enzyme activity of 2,000 FU. This information is important because the amount of nattokinase does not directly correspond to the activity. 2 mg of nattokinase does not necessarily have the same enzyme activity. The maximum activity that a product can currently contain per daily dose corresponds to these 2,000 FU.
As described above, in studies an effective dose is sometimes only assumed to be higher than a higher activity of, for example, 10,000 FU. However, this dose is not currently recommended - especially not without consulting a doctor. For safety reasons, upper limits, especially in the EU, are usually kept quite low - in order to avoid risks and side effects as much as possible. Speaking of which, what side effects does nattokinase have?
Are there any risks or side effects when taking nattokinase?
In general, nattokinase is considered to have few side effects. However, caution is advised when taking blood thinners at the same time, as the effect could be potentiated. Therefore, nattokinase and blood thinners should only be taken together after prior consultation and supervision by a doctor.
Nattokinase alone, however, has been shown to be safe, as a 2016 toxicological study showed⁹. In healthy people, the tolerated dose was significantly higher than the currently recommended dose.
Conclusion on Nattokinase: A promising future
If we summarize all the results to date, it is clear that nattokinase has a promising future and may be useful in supporting therapy. Since research into the enzyme is still in its early stages in some areas, it will take some time before nattokinase is used in everyday practice.
However, supplementing with nattokinase products is definitely worth considering – right?
This article is based on carefully researched sources:
Bibliography
- Peng, Y., Yang, X. & Zhang, Y. (2005). Microbial fibrinolytic enzymes: an overview of source, production, properties, and thrombolytic activity in vivo. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 69, 126–132
- Kurosawa, Y., Nirengi, S., Homma, T. et al. (2015). A single-dose of oral nattokinase potentiates thrombolysis and anti-coagulation profiles. Sci Rep, 5, 11601
- Wu, H., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Xu, F., Chen, J., Duan, L., Zhang, T., Wang, J., & Zhang, F. (2020). Breaking the vicious loop between inflammation, oxidative stress and coagulation, a novel anti-thrombus insight of nattokinase by inhibiting LPS-induced inflammation and oxidative stress. Redox biology, 32, 101500
- The top 10 causes of death. (2020). Who.int. Abgerufen 25. August 2023
- Todesursachen (2023). Statistisches Bundesamt. Abgerufen 5. September 2023
- Kim, J., Gum, S., Paik, J. et al. (2008). Effects of Nattokinase on Blood Pressure: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Hypertens Res, 31, 1583–1588
- Okamoto, A., Hanagata, H., Kawamura, Y. et al. (1995). Anti-hypertensive substances in fermented soybean, natto. Plant Food Hum Nutr, 47, 39–47
- Chen, H., Chen, J., Zhang, F., Li, Y., Wang, R., Zheng, Q., Zhang, X., Zeng, J., Xu, F., & Lin, Y. (2022). Effective management of atherosclerosis progress and hyperlipidemia with nattokinase: A clinical study with 1,062 participants. Frontiers in cardiovascular medicine, 9, 964977
- Lampe, B. J., English, J. C. (2016). Toxicological assessment of nattokinase derived from Bacillus subtilis var. natto. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association, 88, 87–99