Themen dieses Blogartikels:
Table of contents
- What is vitamin B12?
- What function does vitamin B12 have in the body?
- Vitamin B12 & blood formation
- Vitamin B12 & the nervous system
- How does a vitamin B12 deficiency occur and what are its effects?
- Sources of vitamin B12 in food
- What treatment options are there?
- Needs & Supply
- Can you overdose on vitamin B12?
- Tips for vegans
- Different forms of B12
- Sources & Bibliography
What is vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin in technical terminology, is a water-soluble vitamin from the series of vitamin B complexes. The body cannot produce vitamin B12 itself. Therefore, the intake of the vitamin through food is the only way to supply it to the body. Finally, the intestinal mucosa plays a decisive role, because it is from here that the glycoprotein (also called instrinsic factor) formed in the gastric mucosa transports the vitamin into the body1.
Did you know that the body is able to store vitamin B12 in the liver for several years, the only vitamin capable of doing so1?

What function does vitamin B12 have in the body?
Vitamin B12 has many health-promoting functions in the body. Among other things, it is relevant for energy production, DNA repair and synthesis, and also for the central nervous system. One important function, together with other cofactors, is to reduce homocysteine levels in the body. Although homocysteine primarily supports the formation of other amino acids, elevated levels have adverse effects on the body and, in the worst case, can cause diseases such as Alzheimer's or venous thrombosis2.
Vitamin B12 also plays an important role in the formation of red blood cells (erythrocytes). Without sufficient vitamin B12, anemia, i.e., a lack of red blood cells, would occur. This leads, among other things, to a poorer oxygen supply to the target organs2.
Vitamin B12 also has a function in the cell division of other cells and is a cofactor of an enzyme that breaks down fatty acids.
Vitamin B12 & blood formation
Vitamin B12 also plays an important role in the formation of red blood cells (erythrocytes). Without sufficient vitamin B12, anemia, or a lack of red blood cells, would occur. This leads to symptoms such as fatigue , paleness, shortness of breath, and, in severe cases, dizziness or rapid heartbeat.³
Vitamin B12 also has a function in the cell division of other cells and is a cofactor of an enzyme that breaks down fatty acids.
Vitamin B12 & the nervous system
When it comes to the formation of red blood cells (erythrocytes), vitamin B12 also plays an important role. Without sufficient vitamin B12, anemia would occur, i.e., a poverty of red blood cells. Among other things, this leads to a poorer oxygen supply to the target organs2.
Vitamin B12 also has a function in cell proliferation of other cells and is a cofactor of an enzyme of fatty acid metabolism.
How does a vitamin B12 deficiency occur and what is its effect?
The causes
As is already known, the body can only absorb the vitamin in the form of food and this mainly through animal food sources. Vegetarians and vegans in particular must be careful here not to suffer from a deficiency and, if necessary, supplement by means of dietary supplements.
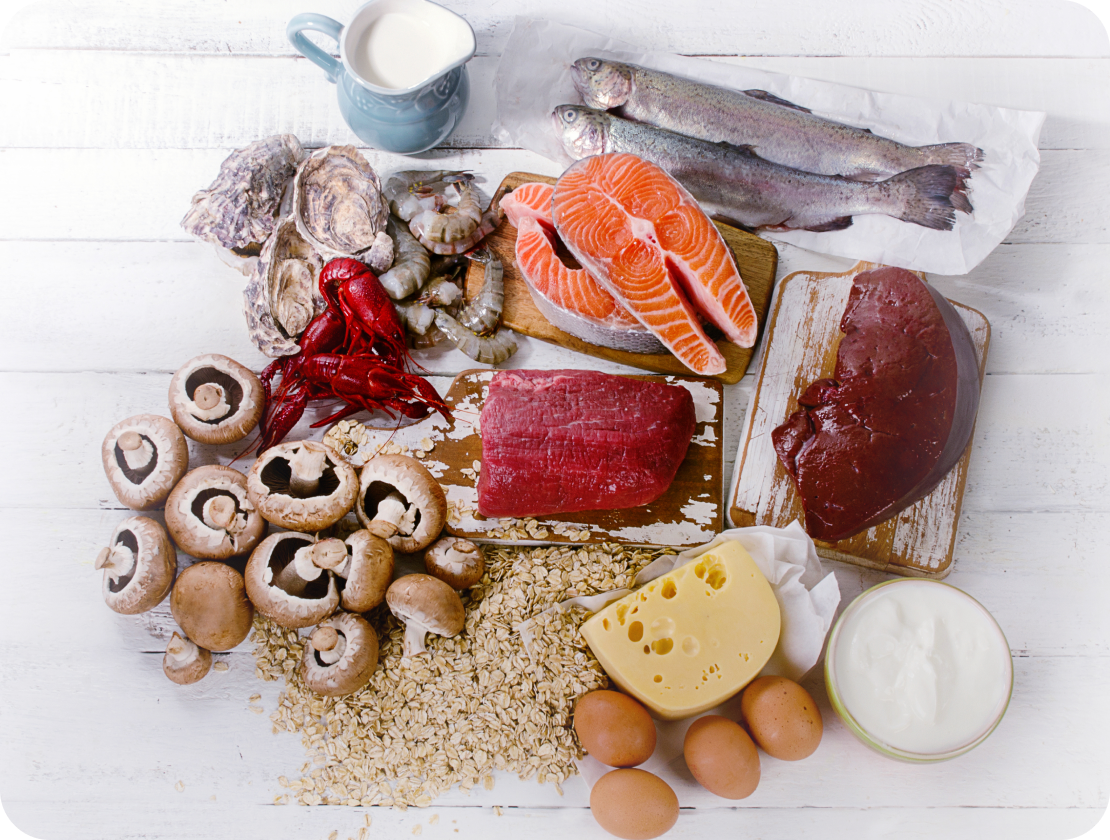


Vitamin B12 sources in food
Vitamin B12 is found almost exclusively in animal foods such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products.⁷ For people with a vegan diet, it is therefore especially important to use fortified products or supplements to meet their daily needs.⁷ Vegan sources include fortified foods such as plant milk or yeast extracts, as well as certain types of algae such as nori.⁷
The symptoms of a vitamin B12 deficiency
There are already a few mild symptoms that indicate a vitamin B12 deficiency. Among other things, these take the form of difficulty concentrating, reduced memory, anemia, fatigue and, in some cases, numbness in the fingers and toes2.
However, just because someone is tired more often for a certain period of time does not mean that they are immediately suffering from a vitamin B12 deficiency. For an accurate diagnosis, it is advisable to see a doctor and have a detailed blood count done.


What treatment options are available?
As mentioned earlier, diet, disease or genetic changes can inhibit or even stop the absorption of the vitamin. Nevertheless, there are ways to supply the body with vitamin B12.
In addition to the intramuscular injection, it is also possible to take vitamin B12 in the form of tablets or capsules. Daily intake of the high-dose vitamin capsules has the same degree of effectiveness as the injections. The only difference is that the intramuscular injection works faster and is therefore more of an option for patients with severe deficiency symptoms or neurological symptoms6. In addition, the digestive tract is bypassed. The injections are particularly useful for people with inflammatory intestinal diseases.

Is it possible to overdose on vitamin B12?
Absorption of vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 absorption occurs in the small intestine and is aided by intrinsic factor, a protein produced in the stomach . Problems with the production of this factor can significantly impair absorption and increase the risk of deficiency.³
Can you overdose on vitamin B12?
It's generally not possible to overdose on vitamin B12 in the body. A healthy body flushes out excess vitamins through the kidneys. However, elevated vitamin B12 levels can be a sign of liver and kidney disease. A doctor is best placed to determine this based on additional laboratory results.⁸
Tipps for vegans
Since even the vitamin B12 traces contained in fruit or vegetables do not cover the daily requirement of vitamins, it is advisable to supplement with the help of supplements.
Different forms of B12
Cyanocobalamin: synthetic form
Cyanocobalamin, short form CNCbl, belongs to the category of the synthetic form of vitamin B12. Due to its special stability, it is a popular ingredient of dietary supplements or medications. However, cyanocobalamin does not occur in natural form and must be obtained artificially. It is also found in the human body only in trace amounts in tissues7. The bioactivity, i.e. the influence on your body, is thus lower, since it must first be converted in order to be used.
Active & natural forms of vitamin B12
Methylcobalamin (MeCbl), adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl), and hydroxocobalamin (HCbl) are among the naturally occurring forms and have long been a popular ingredient in dietary supplements. Some scientists advocate the long-term use of the natural substances for dietary supplements to prevent the formation of cyanide in human tissues, which can happen with the use of CNCbl7.
Also: Methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin are active forms that our bodies can use directly in this way. Thus, they are often considered the best forms for supplementation. Methylcobalamin plays a role in methyl and homocysteine metabolism, while adenosylcobalamin plays a role in fatty acid metabolism.
For the vitamin B12 contained in our products, we mainly use the natural forms methylcobalamin, adenosylcobalamin and hydroxocobalamin.
Cyanocobalamin: The synthetic form
Cyanocobalamin, abbreviated to CNCbl, is a synthetic form of vitamin B12. Due to its exceptional stability, it is a popular ingredient in dietary supplements and medications. However, cyanocobalamin does not occur naturally and must be artificially extracted. Even in the human body, it is only found in trace amounts in tissue.¹² Its bioactivity, or impact on your body, is therefore lower, as it must first be converted to be utilized.
Active & natural forms of vitamin B12
Methylcobalamin (MeCbl), adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl), and hydroxocobalamin (HCbl) are among the naturally occurring forms and have long been a popular ingredient in dietary supplements. Some scientists advocate the long-term use of these natural substances in dietary supplements to prevent the formation of cyanide in human tissue, which can occur with the use of CNCbl.¹²
Furthermore, methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin are active forms that our body can use directly. They are therefore often considered the best forms for supplementation. Methylcobalamin plays a more important role in methyl and homocysteine metabolism, while adenosylcobalamin plays a more important role in fatty acid metabolism.
For the vitamin B12 contained in our products, we mainly use the natural forms methylcobalamin, adenosylcobalamin and hydroxocobalamin.
This article is based on carefully researched sources:
Bibliography
2 What are the functions of B vitamins and vitamin C?(o. D.). https://mitocare.de/blogs/wissensblog/funktionen-wasserloesliche-vitamine.
3 Obeid, R., Heil, S. G., Verhoeven, M. M. A., van den Heuvel, E. G. H. M., de Groot, L. C. P. G. M., & Eussen, S. J. P. M. (2019). Vitamin B12 Intake From Animal Foods, Biomarkers, and Health Aspects. Frontiers in nutrition, 6, 93. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2019.00093.
4 Romain, M., Sviri, S., Linton, D. M., Stav, I., & van Heerden, P. V. (2016). The role of Vitamin B12 in the critically ill--a review. Anaesthesia and intensive care, 44(4), 447–452. https://doi.org/10.1177/0310057X1604400410.
5 Shipton, M. J., & Thachil, J. (2015). Vitamin B12 deficiency - A 21st century perspective . Clinical medicine (London, England), 15(2), 145–150. https://doi.org/10.7861/clinmedicine.15-2-145.
6 Langan, R. C., & Goodbred, A. J. (2017). Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Recognition and Management. American family physician, 96(6), 384–389.
7 Temova Rakuša, Ž., Roškar, R., Hickey, N., & Geremia, S. (2022). Vitamin B12 in Foods, Food Supplements, and Medicines-A Review of Its Role and Properties with a Focus on Its Stability. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 28(1), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010240.