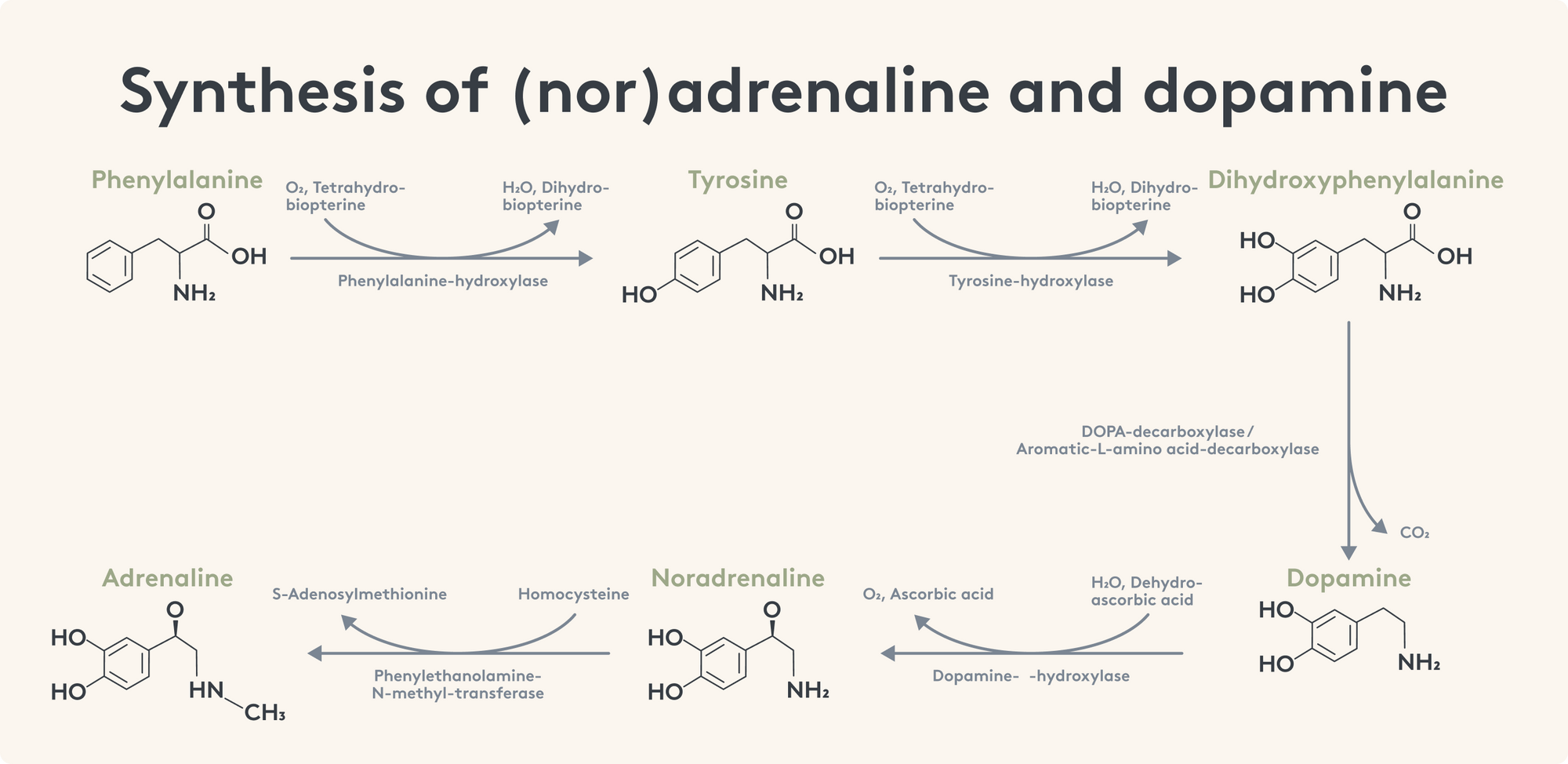
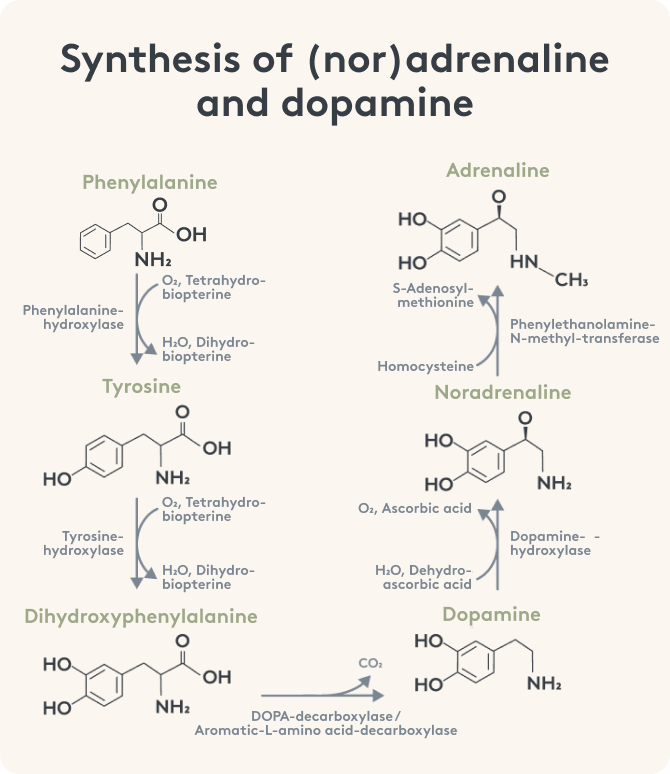
Themen dieses Blogartikels:
Table of contents
- The Basics: What is an Amino Acid?
- Where can you find the building blocks for proteins?
- Meaning and important functions
- Lack of amino acids: These symptoms indicate
- Causes of amino acid deficiency: nutrition and external factors
- Which people are particularly at risk?
- How do amino acids and an active lifestyle fit together?
- How to combat amino acid deficiency
- bibliography
The Basics: What is an Amino Acid?
Amino acids are chemical compounds that consist of an amino group with nitrogen and a carboxylic acid group with oxygen and carbon. Strictly speaking, amino acids are called aminocarboxylic acids. However, the shorter form is more common.
Where do you find the building blocks for proteins?
Amino acids can be found in all living things on earth and play a special role for every organism: They form the basis for proteins , which are involved in almost all processes in your body. That is why amino acids are also referred to as the building blocks of life .
Your cells, muscles and tissue are mostly made up of amino acids. Over 250 amino acids are known - but only 21 of them are considered proteinogenic. This means that these representatives are part of proteins and are therefore essential for biological processes.¹
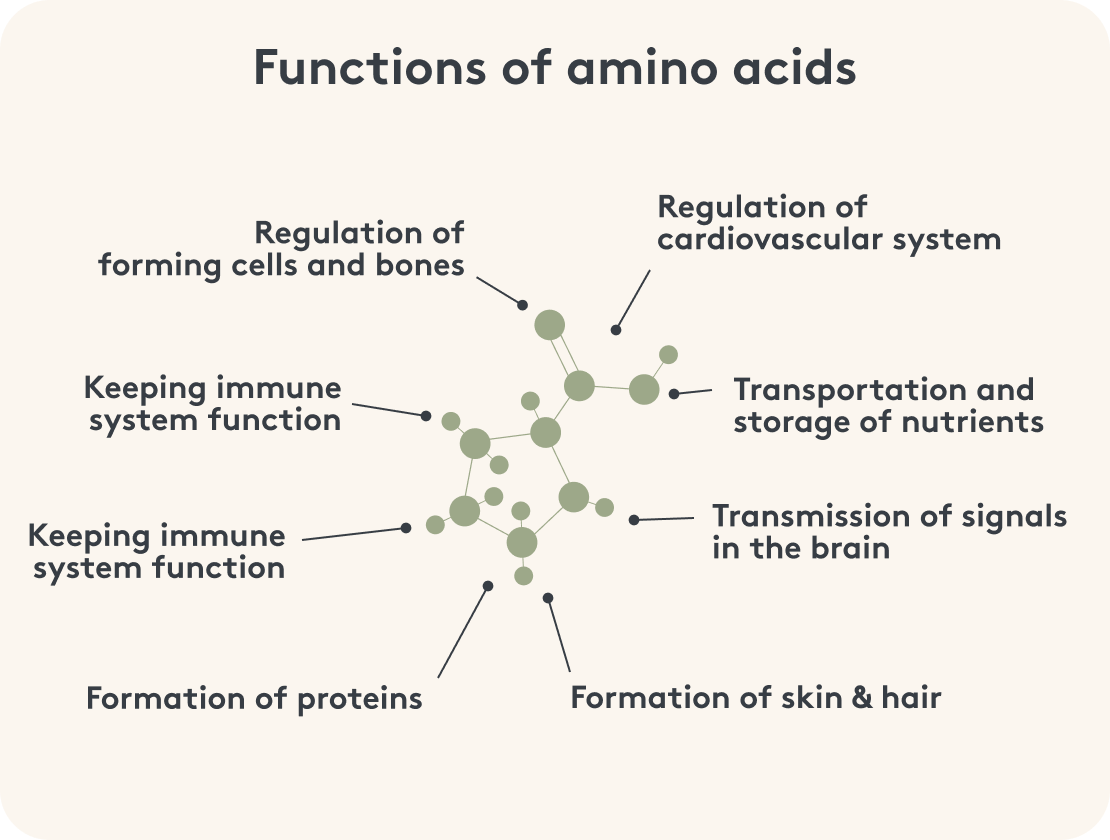
meaning and important functions
Amino acids perform various important functions, including:
- formation of proteins
- structure of skin and hair
- signal transmission in the brain
- synthesis of muscles
- nutrient transport and storage
- regulation of the cardiovascular system and cell and bone structure
- control of hormone production
- maintenance of the immune system
- transport and storage of many nutrients
- Supporting the function of organs, glands, tendons and arteries
- Promoting the healing process of wounds
There are many other tasks that amino acids perform in your body. It is therefore no wonder that an amino acid deficiency can have a negative impact on your well-being - on the one hand on your immune system and on your psyche . But your performance, potency, fat metabolism and blood sugar levels can also suffer from a lack of amino acids.
Therefore, it is important that we take the time to learn more about amino acid supply and the consequences of amino acid deficiency.
Tip: If you want to know exactly what amino acids are and what functions they perform in your body, you will find all the answers in our extensive background article on amino acids .

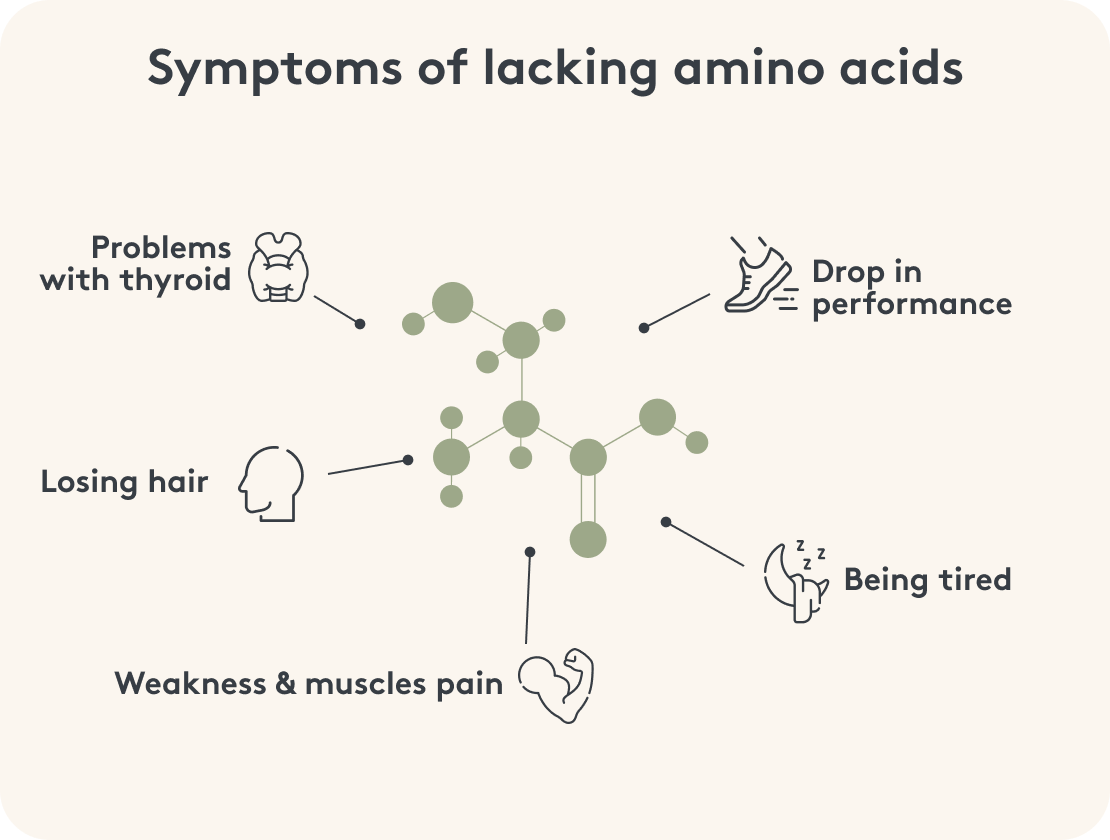
Lack of amino acids: These symptoms indicate
The functions of amino acids in our body are as diverse as the symptoms of an amino acid deficiency. Signs that there is a deficiency in amino acids and therefore in proteins include:
- loss of performance and fatigue
- sleep disorders
- mood swings
- muscle pain
- muscle weakness
- weight gain
- hair loss
- thyroid disorders
- fluctuations in blood sugar levels
The fatal thing is: If you are missing a single amino acid, it affects all proteins.

Causes of amino acid deficiency: nutrition and external factors
In order to understand the causes of a lack of amino acids, we first need to clarify where the body gets them from. It is also important to know that not all amino acids are the same. You have probably heard of essential and non-essential amino acids. This classification provides information about how the protein building blocks are formed:
- Essential amino acids such as lysine , methionine , phenylalanine , threonine and tryptophan – this amino acid is a precursor to the happiness hormone serotonin – are particularly important for your well-being. However, the body cannot produce them itself. You can ensure that you get enough of these amino acids through your diet.
- The body produces non-essential amino acids itself, for example by converting essential amino acids into non-essential amino acids.
- Semi-essential amino acids , which include histidine and arginine, are produced by the body itself. However, the amount of these building blocks for your proteins may not be sufficient during certain phases of life, such as pregnancy.
A balanced diet provides your body with all the important amino acids. But what if symptoms of a deficiency still occur?
Which people are particularly at risk?
In some phases, the supply of amino acids is difficult or insufficient. The following examples show which groups of people may experience an amino acid deficiency because the need for essential amino acids cannot be met through food, for example.
- Pregnant women: Pregnancy is like a rollercoaster ride for the hormones. During this phase, the hormonal balance changes fundamentally, which affects, among other things, the production of semi-essential amino acids. This can lead to a slight deficiency of these amino acids.
- Children: During adolescence, the human body is still growing and is unable to produce the semi-essential amino acids histidine and arginine in sufficient quantities. In addition, the overall need for amino acids is greatly increased during this phase.
- People with chronic illnesses: Chronic illnesses are often accompanied by a lack of nutrients. If amino acids such as arginine and citrulline are missing, this can have negative consequences for blood pressure and blood circulation. The body needs these amino acids, among other things, to regulate the blood vessels.²
- People under stress: Are you exposed to greater stress? Then your body releases stress hormones. The basis for these hormones are the amino acids L-tyrosine and L-phenylalanine.
How do amino acids and an active lifestyle fit together?
Athletes need an intact immune system and strength if they want to achieve their personal goals. A sufficient supply of amino acids is important for performance and prevents, among other things, muscle breakdown. The body needs them for various functions that affect your performance:
- The three essential amino acids L-leucine , L-isoleucine & L-valine, also known as BCAA, promote muscle building and metabolism³ and energy production.
- The amino acid L-carnitine boosts your fat burning and supports muscle regeneration.⁴
- The amino acid L-arginine helps to improve your blood circulation – and thus the development of strong muscles.⁵
- Creatine, which is valued by many athletes, is not an amino acid. However, the body needs amino acids to produce creatine. This is why athletes cannot do without this substance.
A master’s thesis on amino acids in sports has revealed another important finding⁶: Amino acids can have a positive effect on existing pain symptoms and improve general well-being.

How to combat amino acid deficiency
You now know how a deficiency in amino acids arises and which diseases it can lead to. We have also shown which people may have an increased need. With a balanced diet, the intake is usually sufficient and a deficiency in amino acids is unlikely.
But what should you do if you notice deficiency symptoms or an increased need for amino acids? For pregnant women, growing children or competitive athletes, it is important to recognize a deficiency and adjust the supply through food accordingly. Since athletes have an increased need for amino acids, they should, for example, include as much protein as possible in their diet.
In addition, if you have an amino acid deficiency, it may be worth considering supplementation . You can prevent a deficiency with high-quality products . Such preparations contain not only essential amino acids, but also vitamins and minerals that offer positive synergistic effects.
Reading tip: If you want to learn more about how to shape your diet and thereby improve your well-being, you will find valuable background information in our nutrition blog .
This article is based on carefully researched sources:
bibliography
- bfr.bund.de/de/gesundheitliche_vergleich_von_aminosaeuren-54420.html
- Allerton, TD, Proctor, DN, Stephens, JM, Dugas, TR, Spielmann, G., & Irving, BA (2018). l-Citrulline Supplementation: Impact on Cardiometabolic Health. Nutrients, 10(7), 921.
- Plotkin, DL, Delcastillo, K., Van Every, DW, Tipton, KD, Aragon, AA, & Schoenfeld, BJ (2021). Isolated Leucine and Branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation for Enhancing Muscular Strength and Hypertrophy: A Narrative Review. International journal of sport nutrition and exercise metabolism, 31(3), 292–301.
- Gnoni, A., Longo, S., Gnoni, GV, & Giudetti, AM (2020). Carnitine in Human Muscle Bioenergetics: Can Carnitine Supplementation Improve Physical Exercise? Molecules, 25(1), 182.
- Khalaf, D., Krüger, M., Wehland, M., Infanger, M., & Grimm, D. (2019). The Effects of Oral l-Arginine and l-Citrulline Supplementation on Blood Pressure. Nutrients, 11(7), 1679.
- sportaerztezeitung.com/rubriken/ernaehrung/4263/aminosaeuren/