Themen dieses Blogartikels:
Table of Contents
- Definition: What is creatine?
- Production & occurrence of creatine in the body
- How does creatine work?
- Importance of Creatine in Training
- More strength with creatine
- Does creatine affect your muscle building?
- What is the best way to take creatine?
- Creatine as a dietary supplement: What dosage is recommended?
- Are there any side effects?
- Monopreparation or complex product: How should I take creatine?
- Sources & Bibliography
Definition: What is creatine?
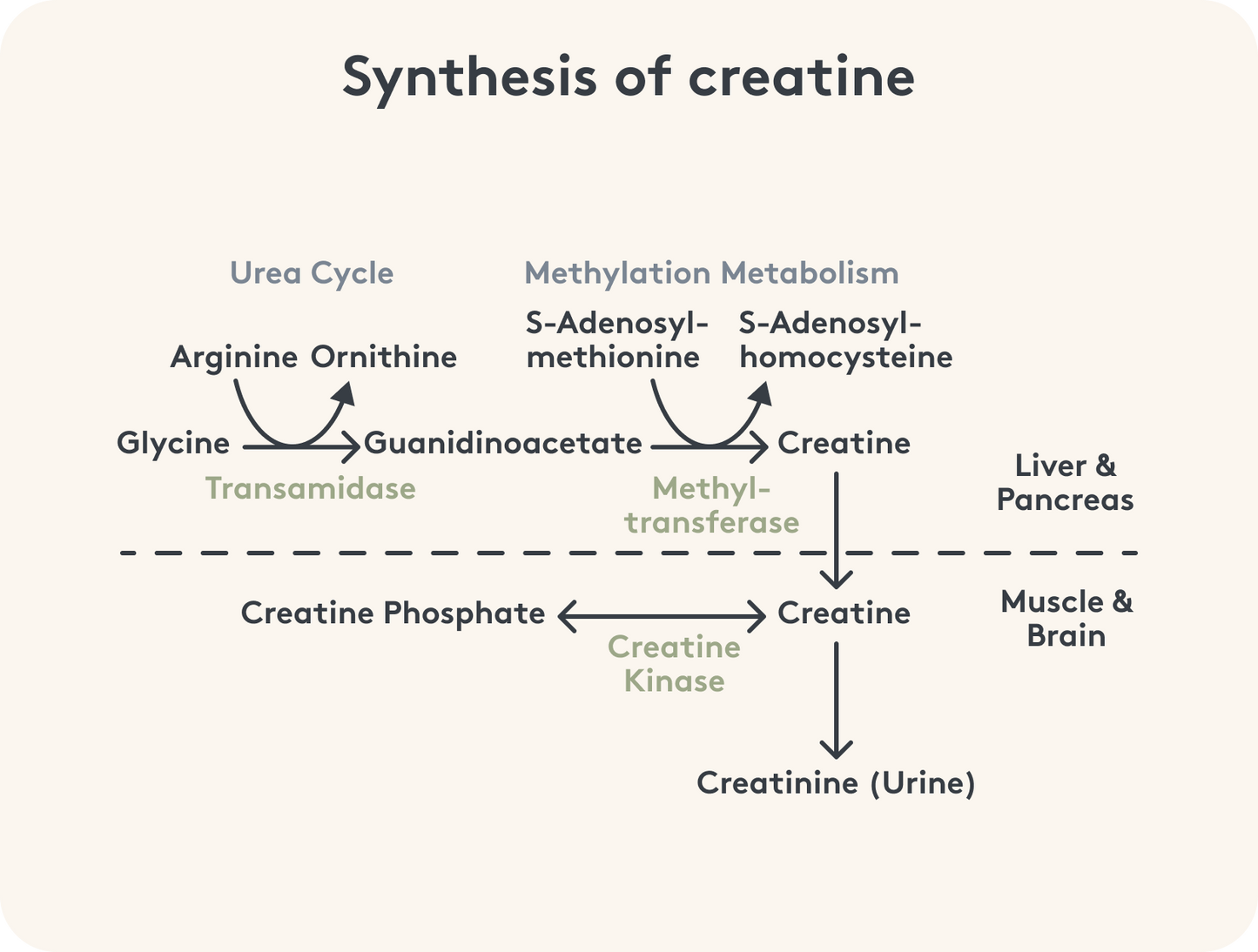
Creatine is an organic compound that has similarities to the protein building blocks amino acids , but is not an amino acid in the true sense. The substance that is sometimes also called creatine is, however, based at least on the protein building blocks arginine, glycine and methionine .
Your body is able to produce this substance in small amounts itself, for example in the liver, kidneys and pancreas. The organism needs about two grams of creatine every day, of which about one gram per day comes from its own production.¹ The body obtains the rest from food.
Creatine does not remain creatine: In order to be effective, the creatine produced and ingested is converted into creatine phosphate in the muscles.
Production & Occurrence of Creatine in the Body
How much creatine you can actually produce yourself depends on whether all the required substances are available in sufficient quantities. The body needs methionine in particular, which is converted to SAMe (S-adenosylmethionine), for many other purposes. If there is too little of it, the organism first saves on creatine synthesis.
Incidentally, 95 percent of the creatine storage is located in the muscle cells.² Two thirds of the substance is available in the form of creatine phosphate.

How does creatine work?
The fact that creatine is mainly found in muscle tissue already indicates that the compound plays an important role in building muscle and increasing your strength. So let's take a closer look at the effects of creatine.
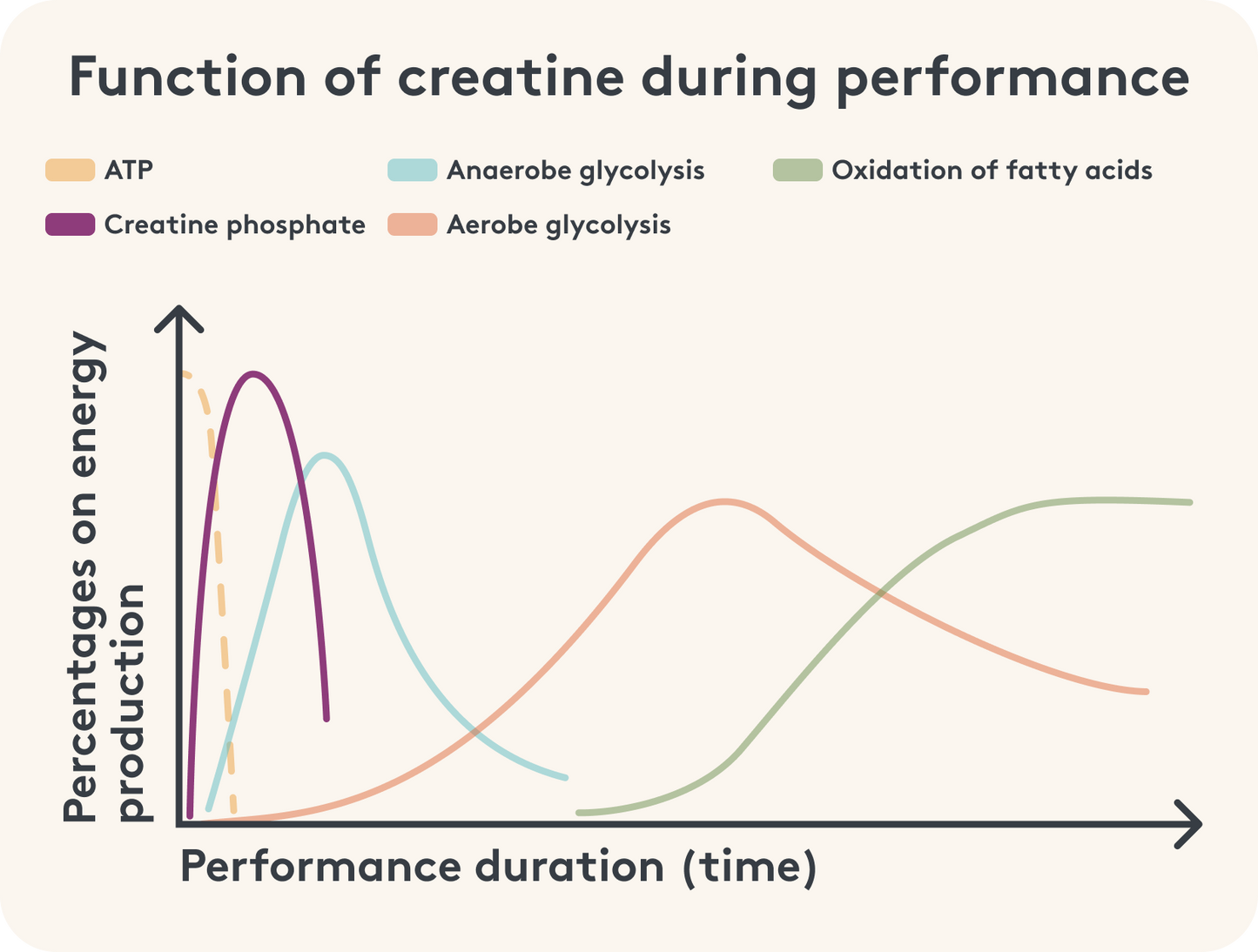
When you tense your muscle tissue during a sport such as strength training, it needs energy to maintain the contraction. Your body uses energy in the form of the energy carrier adenosine triphosphate, or ATP for short.
There is a problem, however: after just a few seconds, the energy reserves are used up and your muscles run out of steam. This is where creatine comes into play in the form of creatine phosphate. The phosphate ensures that ATP is regenerated and your muscles can continue to contract without having to tap into another source of energy.
Importance of Creatine in Training
The process just described is particularly relevant in strength training, where energy is needed quickly, especially during intense and short periods of exertion such as weight lifting. This energy comes first from anaerobic energy production, i.e. the body produces energy without oxygen.
In the process, glucose is converted into lactate. This acidic molecule must be transported to the liver via the blood. If there is a particularly high amount of it, it can impair muscle building - because the acidic product can lead to over-acidification of the muscle. Lactate can accumulate in the muscle and lead to a burning sensation and a temporary reduction in performance during training.
More Strength with Creatine
Creatine plays an important role here because it helps the muscles to provide energy quickly and in the short term before the body has to resort to glucose. After a few minutes, the muscle ideally switches again - then oxygen is used to generate energy.
To summarize: If the start of anaerobic energy production is delayed, lactate production is also delayed and the contraction can be maintained for a longer period in a less stressful manner. This is particularly advantageous for strength training - because for strength athletes the strain is particularly intense and short-term.

Does creatine affect your muscle building?
Yes, because creatine influences energy production in the muscles and delays fatigue, it can be beneficial for building muscle mass.³ Further effects in muscle cells are still being investigated in studies. However, it is possible that creatine also supports muscle building by changing the activity of certain genes.⁴
Creatine also promotes water retention in the muscles, thereby creating the typical "pump effect" that is usually desirable during strength training. It has even been shown to improve physical performance.⁵ This increase in physical performance can, in turn, also lead to an increase in the intensity of training and thus to faster muscle building .
What is the best way to take creatine?
You can take in creatine through food. The substance is found in meat and fish, for example. It is also possible to fill up your creatine stores with the help of food supplements if you are planning particularly intensive workouts. You typically take creatine monohydrate . This is the most common active ingredient and the one used in most studies on the effects of creatine.
Advertisement
- All-in-one amino acids & vitamin complex with creatine
- Galactose, D-tagatose & smart amino acid glycine instead of sugar
- Best-selling product & top reviews
- 11 premium amino acids & manganese
- With zinc, vitamin C & B6 In powder form
- For your recovery & nighttime regeneration
- Developed with doctors & experts

Creatine as a dietary supplement: What dosage is recommended?
Whether as a powder or in capsule form, the amount taken depends on your weight. We recommend taking 3 to 5 grams of creatine per day.
Incidentally, women in particular often fear that their muscles will become “too big” or that their body structure will change when they take creatine. We can reassure you here: creatine does promote muscle growth and is stored in the muscles. However, the entire body does not change. body, since creatine is not a steroid or anything like that.
Are there any side effects?
Creatine is considered a safe dietary supplement, so there is no great risk of overdose. It is often stated that high doses can cause kidney problems, but these are isolated cases, so this argument can be refuted in good conscience.⁶ It is important to always drink enough water when taking creatine.
Monopreparation or complex product: How should I take creatine?
At MITOcare, we design our nutritional supplements to be as close to nature as possible in all its complexity. That's why you'll find creatine in some of our products - often in combination with amino acids and other substances that support connective tissue and muscles. Of course, you can also take creatine as a standalone product. But why, when you can cover several nutrients with one product?
Regardless of whether you are a competitive athlete or are just starting to optimize your performance: If you are looking for more tips for better performance and a balanced diet and want to know what else you need for your well-being besides creatine, take a look at our blog. Enjoy reading!
This article is based on carefully researched sources:
Sources & Bibliography
- Berger, C. (2009). Dietary supplements and selected substances using women as an example. Diploma thesis. University of Vienna.
- Schek, A. (2000). Creatine supplements for everyone? Sports Medicine, 2, 58-62.
- Wu SH, Chen KL, Hsu C, et al. (2022). Creatine Supplementation for Muscle Growth: A Scoping Review of Randomized Clinical Trials from 2012 to 2021. Nutrients, 14(6), 1255.
- Farshidfar F, Pinder MA, Myrie SB (2017). Creatine Supplementation and Skeletal Muscle Metabolism for Building Muscle Mass- Review of the Potential Mechanisms of Action. Current protein & peptide science, 18(12), 1273–1287.
- Izquierdo, M., Ibañez, J., González-Badillo, JJ, & Gorostiaga, EM (2002). Effects of creatine supplementation on muscle power, endurance, and sprint performance. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 34(2), 332–343.
- Kreider RB, Kalman DS, Antonio J et al. (2017). International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: safety and efficacy of creatine supplementation in exercise, sport, and medicine. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 14(1).



















