Themen dieses Blogartikels:
Table of contents
- Why oils are essential
- Oils as an energy source & hormone building block
- Omega-6 fatty acids: curse or blessing?
- Refined oils: What's behind them & how do they work?
- Oils for different life stages & needs
- Athletes & Active People
- Pregnant & Breastfeeding
- Vegetarian
- Mature Adults & Seniors
- Mental Focus & Office Athletes
- Which oils are suitable for which time of year?
- Practical application ideas for your everyday life
- Oil Overview: The Most Important Oils Compared
- Frequently Asked Questions - Answered Briefly
- Quality & Storage: How to get the most out of your oil
- Oils & Nutritional Styles: Keto, meditation, vegan - find out which one suits you.
- Sources & Bibliography
Introduction
Healthy oils are indispensable in a balanced diet – edible oils are the focus of this article – but which oil is right for you and your goals? This comprehensive guide explains why high-quality vegetable and functional oils, especially various vegetable oils, are essential for your body, which oils give you focus, energy, and cell health , and how to use them optimally in everyday life. Whether you are physically active, eat a vegan diet, are pregnant, or simply pay attention to your health – here you will find differentiated recommendations , application tips, and a clear comparison of the most important oils from seeds, nuts, oilseeds, and various oil fruits. Salt, besides edible oils, is another basic spice that should not be missing in any kitchen. Let's find out together which oil – for example, a vegetable oil – is best suited to which need and time!
"Oils, oils, oils" - explained by our founder
Our founder, Christian Burghardt, is convinced that oils can make a significant contribution to your well-being. In his short video, he explains how important oils are for your cell membranes and nutrient absorption.
Why oils are essential
Oils (and fats in general) are far more than just flavor carriers – they perform vital functions in your body. As a macronutrient, fats provide a lot of energy with about 9 kcal per gram – more than double that of proteins or carbohydrates.¹ But calories aren't everything: without fat, your body couldn't function properly. Besides oils, there are also edible fats, which are mostly solid and differ from edible oils in their production, composition, and use.
- Building blocks of the cell membrane : Each of your cells is surrounded by a double layer of lipids. This cell membrane needs fat to remain flexible and intact. Fatty acids – especially the essential fatty acids omega-3 and omega-6 – are crucial for the structure and fluidity of cell membranes.² Good quality fats in the diet directly influence the composition and mobility of your cell membranes and thus the communication between cells.² Many edible oils are obtained from seeds, nuts, oilseeds or oil fruits of plants, which significantly determines their nutrient composition and quality. Cell health therefore begins with the right fat intake!
- Transport of fat-soluble vitamins: Vitamins such as vitamin A , vitamin D , vitamin E , and vitamin K are fat-soluble, meaning your body can only absorb them if sufficient fat is present as a carrier. Without sufficient oil in your diet, these vitamins would hardly enter your bloodstream.¹ Vitamin E – abundant in nuts and vegetable oils – acts as a cell-protective antioxidant, but needs fat as a transport vehicle.¹ Nuts are not only a valuable source of vitamin E , but also provide other important nutrients and can be used in a variety of ways in the diet. A dash of healthy oil in your salad ensures that you optimally absorb the vital nutrients from vegetables.
Good to know: Fats are vital! They provide concentrated energy, form cell structures, transport vitamins and protect the body. Cholesterol is not only an important component of the cell membrane , but also a fat-associated substance that serves as a building block for hormones. Fat-associated substances in vegetable oils also include secondary plant substances, fat-soluble vitamins and other bioactive components that increase their nutritional value. In the next step, we will look at how oils influence your energy metabolism and hormone balance . Vegetable oils play a central role in a balanced and healthy diet.
Oils as an energy source & hormone building block
Fats are efficient energy suppliers . Especially during prolonged exertion or when carbohydrate stores are depleted, your body draws on fat reserves.² Oils as an energy source have the advantage of releasing energy slowly and evenly – ideal for long-lasting power. There are different types of edible oils, such as cold-pressed, refined, or oils obtained from different plant sources, which differ in their composition and energy release. One gram of fat provides about 9 kilocalories of energy.¹ Therefore, a tablespoon of oil (approx. 15 g) can contain around 135 kcal – that sounds like a lot, but this energy is also released slowly. Medium-chain fatty acids (more on that later) in particular are quickly converted by the body into ketone bodies , an alternative energy source for the brain and muscles.³ So a morning coffee with MCT oil can give you a quick energy boost and mental focus.³
But oils don't just provide fuel – they are also building blocks for hormones . Many hormones (such as sex hormones like estrogen or testosterone) are based on cholesterol , a fatty substance.⁴ Your body produces cholesterol in the liver and uses it to form vitamin D, bile acids, and hormones.⁴ Without enough fat in your diet, hormone production can stall. Fats also influence hormone-like eicosanoids , which are derived from omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids and regulate inflammation.² Omega-6 fatty acids are an important part of the diet, as they are necessary for the formation of certain eicosanoids and the maintenance of various bodily functions. Vegetable oils such as thistle oil, sunflower oil, grape seed oil and pumpkin seed oil are particularly rich in omega-6 fatty acids, and therefore make a significant contribution to the fatty acid balance in the diet. Omega-3 provides more anti-inflammatory signaling molecules, omega-6 more pro-inflammatory – both are necessary, but the ratio should be right (ideally a maximum of 4:1 in favor of omega-6).²
In short: Fats in the diet keep your metabolism and hormone balance in equilibrium. They ensure energy supply – especially during periods without food or during endurance exercise – and provide the basic materials for essential hormones and signals.²
Tip: Don't be afraid of fat! The quality and method of production are crucial. Unsaturated fatty acids from vegetable oils are considered heart-healthy because they can improve cholesterol levels and reduce inflammation.⁵
Omega-6 fatty acids: curse or blessing?
Omega-6 fatty acids are a staple component of many vegetable oils – for example, sunflower oil, rapeseed oil, and olive oil. This type of polyunsaturated fatty acid is indispensable for our bodies: they keep blood vessels supple, support blood clotting, and are involved in numerous metabolic processes. A balanced proportion of omega-6 fatty acids in the diet helps ensure that our organs function optimally and our cells remain flexible.
However, as with everything, it's all about the right balance. Too high a proportion of omega-6 fatty acids – for example, through excessive consumption of certain oils or processed foods – can promote inflammatory processes in the body. This is because omega-6 fatty acids can serve as a starting material for inflammatory mediators. Therefore, it is important to keep an eye on the ratio of omega-6 to omega-3. An ideal ratio is a maximum of 4:1, so that the positive properties of both types of fatty acids can be optimally utilized.
How can you achieve this in everyday life? Opt for a colorful mix of different vegetable oils: For example, use rapeseed oil or olive oil for daily use, occasionally supplement with sunflower oil, and make sure to regularly incorporate omega-3 -rich oils such as linseed oil or walnut oil. This way you benefit from the advantages of each type of fatty acid and support a balanced, varied diet.
Advertisement
- Organic extra virgin olive oil (Omega 9 fatty acid) from Calabria, Italy
- From controlled organic cultivation, without pesticides & artificial fertilizers
- 11 valuable fatty acids
- Careful harvesting of the olives
- Gentle cold centrifugation process <27°C - ensures preservation of aromas & polyphenols
- Mild-fruity oil without additives
- Organic quality, vegan & vegetarian
- Developed with doctors & experts

Refined oils: What's behind them and how do they work?
We encounter refined oils in the kitchen every day – but what's actually behind them? Unlike cold-pressed oils, refined oils are obtained from oilseeds such as rapeseed, sunflower, or soy using heat and special purification processes. This removes unwanted substances, resulting in an oil that is particularly clear, odorless, and tasteless. This makes refined oils true all-rounders: they are versatile, have a long shelf life, and are excellent for frying, baking, or deep-frying.
However, refining also has its downsides. The processing leads to the loss of many valuable plant substances and vitamins that are still present in cold-pressed oils. Nevertheless, refined oils provide the body with readily available energy and are indispensable in modern nutrition. They offer a practical base for many dishes and are ideal when a neutral aroma or high heat stability is required. Those who value a balanced diet can purposefully combine refined oils with high-quality, cold-pressed oils – this way you get the best of both worlds.
Oils for different life stages and needs
Everyone is different – so it's worth choosing the oils that best suit your current lifestyle, age, or special circumstances . For example: Linseed oil, due to its high omega-3 content, is particularly suitable for athletes as a supplement in salads or muesli. Here's an overview of which oils are particularly recommended for which target groups:
Advertisement
- Cold-pressed organic flaxseed oil made from high-quality, organic flax seeds.
- Contains the important omega-3 fatty acid ALA (alpha-linolenic acid)
- Flax seeds from controlled organic cultivation - Naturland-certified organic flaxseed
- Gentle cold pressing after harvesting allows for the preservation of valuable ingredients <40°C
- 8 different fatty acids in their natural form, vegan & vegetarian
- Without fillers or flavorings
- Developed with doctors & experts

Athletes & Active People:
If you train a lot or have an active lifestyle, you benefit from oils that provide quickly available energy. MCT oil is the secret tip here: These medium-chain fatty acids are transported directly to the liver without detour and quickly converted into energy (ketone bodies) – good for mental focus and powerful muscles.³ Many athletes appreciate MCT oil in a shake or coffee before training for a quick energy boost. MCT oil also has slightly fewer calories per gram than conventional fats.⁶ Some oils, such as MCT oil or flaxseed oil, contain a high proportion of certain fatty acids, which makes them particularly valuable for athletes. Omega-3 is also important for athletes: It can support regeneration and reduce inflammation after intensive workouts.⁷ This is where flaxseed oil, walnut oil or algal oil come into play – they supply you with omega-3 fatty acids and support cardiovascular health.⁷


Pregnant & Breastfeeding:
During pregnancy, the need for certain fatty acids increases significantly. In particular, DHA , an omega-3 fatty acid, is important for the development of the baby's brain and eyesight.⁸ The German Nutrition Society (DGE) recommends an additional 200 mg of DHA per day for pregnant and breastfeeding women.⁹ If you don't eat fatty fish, algal oil is the ideal vegan omega-3 source – it provides DHA and EPA in a readily available form.⁸,¹⁰ In addition, linseed oil, rapeseed oil, and walnut oil can provide the omega-3 precursor ALA; however, the body's own conversion into DHA/EPA is limited.⁸
Vegan:
Without fish and other animal products, it is particularly important to consume sufficient Omega-3 . Algae oil is the top choice here, as it provides – just like fish oil – the valuable long-chain Omega-3 fatty acids DHA and EPA , only in a purely plant-based form.⁸,¹⁰ Those who don't use algae oil should incorporate flaxseed, hemp, walnut, or rapeseed oil daily to supply ALA (alpha-linolenic acid) – however, the most reliable way is the direct intake of DHA/EPA via algae oil.⁸,¹⁰
Advertisement
- 2-in-1 blend of olive oil & algae oil
- Combines the important fatty acids DHA & EPA from plant-based algae oil.
- Daily dose with 800mg DHA & 450mg EPA in a 2:1 ratio
- Plant-based & sustainable alternative to fish oil
- Mild flavor for integration into cold dishes
- Without fillers or flavorings
- Developed with doctors & experts
- Vegan & vegetarian

Best Ager & Seniors:
Heart-healthy oils gain in importance with age. Extra virgin olive oil – the cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet – can help prevent cardiovascular diseases. Regular consumption is associated with lower mortality and fewer cardiovascular events in cohort studies.¹¹ Omega-3 (DHA/EPA) additionally supports brain function; algal oil is a convenient, low-contaminant option here.⁸ Walnut oil (rich in Omega-3) and hemp oil (with GLA) can also support blood vessels, skin, and joints.¹²
Mental Focus & Office Athletes:
Do you need a clear head and focused energy for long working days? Many rely on MCT oil . MCTs increase the production of ketones, which serve the brain as a quick energy source – initial studies show cognitive benefits in mild impairments.³ Besides MCT, it's worth incorporating walnut oil and flaxseed oil : The omega-3 fatty acids promote long-term brain health.¹²,¹³
Of course, many recommendations overlap – after all, everyone benefits from omega-3 and unsaturated fatty acids. Prioritize according to your goal: quick energy & focus → MCT oil , heart & inflammation ↓ → olive/omega-3 oils , vegan pregnancy → algal oil (DHA) .


Which oils are suitable for which time of year?
Not only which oil you use, but also when, can make a difference:
- Morning – Energy & Focus: Bulletproof Coffee with 1 tsp–1 tbsp MCT oil provides ketones as brain fuel – many report clear concentration without cravings.³,⁶ Flaxseed oil fits in muesli, smoothies or yogurt and directly supplies you with ALA-Omega-3.¹³
- Lunch – Nutrient Booster: A salad for lunch? Olive oil improves the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and provides polyphenols.¹ Refined rapeseed oil is ideal for gentle frying; flaxseed or hemp oil are excellent in green smoothies (do not heat).¹
- Before sports – power boost: 1–2 hours before training, MCT oil in a shake provides a quick energy boost without feeling heavy in the stomach.³,⁶ Gradually increase dosage (to ensure stomach tolerance).⁶
- After sports – Regeneration: A meal with some olive oil or omega-3 oil supports inflammation resolution and regeneration.⁷
- In the evening – cell protection & satiety: Olive oil and walnut/hemp oil refine steamed vegetables, salads & bowls – easy to digest, rich in unsaturated fatty acids and antioxidants.¹¹,¹²
- Pay attention to heat stability: For searing, refined rapeseed oil , high-oleic sunflower or peanut oil (high smoke point) are suitable. Cold-pressed oils (e.g. extra virgin olive oil, linseed, hemp, walnut oil) are better used cold or at medium heat.¹
Advertisement
- 300 ml Premium Natural Omega 3 Oil from sustainable wild catch
- 1460mg EPA and 910mg DHA
- Natural 1.6:1 ratio
- Fatty acid complex consisting of 27 fatty acids
- Citrusy, pleasant taste, no fishy taste.
- Total oxidation value <10 & free of heavy metals & Co.
- Laboratory tested
- Developed with doctors & experts

Practical application ideas for your everyday life
- Bulletproof Coffee: Mix 1 tsp of MCT oil into hot coffee (optional with a little butter or plant-based drink) – creamy, focusing. Increase dose slowly.³,⁶
- Smoothie booster: 1 tbsp flaxseed or hemp oil in green smoothies (spinach, cucumber, apple) – better vitamin absorption & omega-3 boost.¹
- Salad dressings & dips: Olive oil as a base, plus walnut oil for a nutty flavor. Linseed oil goes perfectly with quark/potatoes – traditional and rich in Omega-3.¹³
- Frying, stewing & baking: Refined rapeseed oil is your all-rounder for frying, stewing vegetables or baking (neutral, heat-stable). Refined oils are also very well suited for frying, as they can withstand high temperatures. Coconut oil is suitable for medium heat and baked goods with a subtle coconut flavor.¹
- Enjoy it pure: 1 tablespoon of flaxseed oil covers the daily ALA requirement; algal oil directly provides DHA/EPA – practical for vegans and during pregnancy (DHA target 200 mg/day in addition).⁸,⁹,¹⁰,¹³
Cooking oils can be used in a variety of ways to prepare a wide range of dishes – whether for refining, frying, stewing or deep-frying, they bring flavour and valuable nutrients to your dishes.
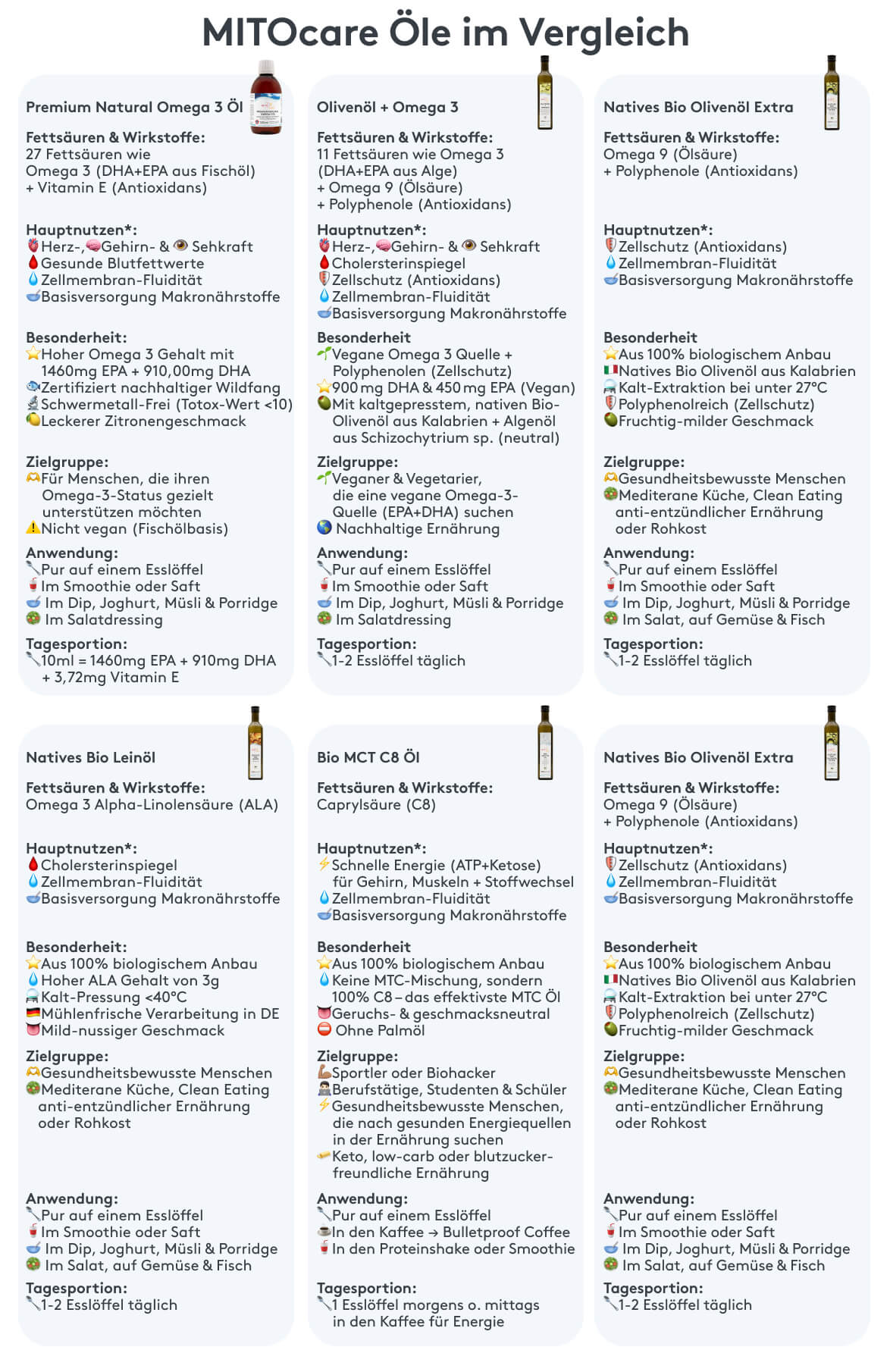
Oil Overview: The Most Important Oils Compared
- MCT Oil: What? Medium-chain triglycerides (mainly C8/C10). Effect: Fast ketones → focus & energy , especially with low-carb/keto.³ Consistency: MCT oil is liquid and very light at room temperature, making it particularly pleasant to use. Application: 1 tsp–1 tbsp in coffee/shakes; do not heat to high temperatures; increase dose slowly.⁶
- Coconut oil (virgin): What? High proportion of saturated fats (lauric acid). Consistency: Coconut oil is solid at room temperature and only melts at about 24°C, making it versatile. Effect: Heat-stable, mild; use in moderation. Application: Baking, gentle frying.
- Extra virgin olive oil: What? Oleic acid + polyphenols. Aroma: Olive oil convinces with its characteristic, fruity aroma, which gives many dishes a special touch. Color: The green-golden color is a quality feature and indicates freshness and gentle processing. *Effect:* Heart protection , anti-inflammatory; ½ tbsp/day associated with a lower mortality risk.¹¹ Application: Cold & moderate heat.
- Flaxseed oil: What? An ALA-Omega-3 powerhouse. Color: The golden yellow color of flaxseed oil is typical and stands for high quality. Effect: Inflammatory modulating; particularly useful with low fish consumption.¹³ *Application:* Cold-pressed only ; fresh, chilled, consume quickly.
- Algae oil: What? Plant-based DHA/EPA . Color: Algae oil is usually light yellow and clear, indicating the purity of the oil. Effect: Heart, brain, eyes; ideal for vegans/pregnant women.⁸,⁹,¹⁰ Application: Take capsules/oil cold .
- Hemp oil: What? Omega-6:3 ~3:1 + GLA . Color: Hemp oil has a greenish color, which is due to the chlorophyll and carotenoids it contains. Effect: Skin/joints, anti-inflammatory.¹² Application: Cold in dressings, bowls.
- Rapeseed oil: What? All-rounder: Rich in oleic acid, ALA, vitamin E. Effect: Heart-healthy; refined, good for frying (high heat tolerance).¹ Refined oils like rapeseed oil are particularly heat-stable and have a long shelf life because unwanted components are removed. Color: Rapeseed oil is usually light yellow and clear, which indicates good quality.
- Walnut oil: What? ALA-Omega-3 + Polyphenols. Aroma: Walnut oil is characterized by its nutty, intense aroma, which gives salads and cold dishes a special flavor. Color: The golden-yellow to brownish color is typical of high-quality walnut oil. Effect: Vascular protection, "brain food".¹² Application: Cold for salads, finishing.
Many edible oils are derived from various vegetable oils and oilseeds. The nutritional properties, the content of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, and the aroma depend significantly on the respective source and the type of oilseeds used.
Cold pressing: Cold-pressed oils are produced without heating, which preserves aroma, vitamins, and fatty acids as well as possible. In contrast, refined oils have unwanted substances removed during the production process, which increases shelf life and heat resistance, but reduces the aroma and some ingredients. The differences between cold-pressed and refined oils therefore concern taste, ingredients, and culinary applications.
Pay attention to the ratio: Most people consume too much Omega-6 and too little Omega-3. A ratio of ≤ 4:1 (Omega-6:Omega-3) is considered favorable – with olive, rapeseed, flaxseed, walnut, hemp and algae oil you are well equipped.²>
Frequently Asked Questions – Briefly Answered
- Healthy oil for frying? Refined rapeseed oil : heart-healthy, high smoke point, neutral.¹
- Vegan Omega-3? Algae oil (DHA/EPA) is the best vegan source; flaxseed/walnut/hemp oil provide ALA (precursor).⁸,¹⁰,¹³
- Best olive oil? Extra virgin , cold-pressed, fruity-green, slightly peppery (polyphenols). Quality & storage matter.¹¹
- Daily dose of Omega-3? Generally 250 mg EPA + DHA/day ; during pregnancy/breastfeeding additionally ~200 mg DHA/day.⁷ ,⁹
Quality & Storage: How to get the most out of your oil
With oils, quality determines taste, effect and stability. Look for organic , cold-pressed and (for olive oil) extra virgin . A fruity-green, slightly peppery taste is a good sign of polyphenols – precisely those secondary plant compounds that are associated with cardiovascular benefits.¹¹
Storage: Sensitive, omega-3-rich oils (flaxseed, walnut, hemp oil) should always be stored cool, dark, and tightly closed – ideally in a cool, dark room such as a pantry or closed cupboard, alternatively in the refrigerator. Use quickly after opening (flaxseed oil usually within 4–8 weeks), as ALA oxidizes quickly.¹³ Heat-stable all-rounders such as refined rapeseed oil can be used at higher temperatures; cold-pressed oils are reserved for cold cooking or moderate heat.¹
For high-quality edible oils, the regional and sustainable cultivation of oilseeds is crucial, as it significantly influences the quality and freshness. Production in a traditional oil mill also guarantees gentle processing and continuous quality assurance.
MCT oil is relatively oxidation-stable and tasteless – perfect for coffee or shakes; do not fry at high temperatures.³ ⁶
Pro-tip: Buy smaller bottles of sensitive oils, open them one after the other, and use dark glass. This minimizes light, oxygen, and heat damage – and you get the full effect of your oils.¹ ¹³
Oils & Dietary Styles: Keto, Mediterranean, Vegan – Find the Right One for You
- Keto & Intermittent Fasting: Use MCT oil for fast ketosis and focused energy – in your morning coffee or in a shake 60–120 minutes before your workout . Increase the dose slowly (e.g., start with 1 tsp) to test your tolerance.³ ⁶
- Mediterranean cuisine: Extra virgin olive oil forms the basis. It provides oleic acid and polyphenols and is associated with lower overall and cardiovascular mortality in cohort studies. A simple, effective step is to consume ½–1 tablespoon daily in salads, vegetables, or bowls.¹¹
- Vegan & vegetarian: Algae oil directly provides you with DHA/EPA – ideal if you don't eat fish or want to cover the additional DHA requirement (~200 mg/day) during pregnancy/breastfeeding . Supplement with flaxseed/walnut/hemp oil for ALA variety, but remember: The body's own conversion of ALA to DHA/EPA is limited – algae oil delivers the target omega-3s directly.⁸ ⁹ ¹⁰ ¹³
- Sports & Recovery: Combine MCT oil pre-workout (fast energy) with Omega-3s in your post-workout meal (e.g., olive oil + algae oil) to support inflammation resolution and recovery.⁷
- Best Ager: Olive oil (rich in polyphenols) + Omega-3 (DHA/EPA) support vascular and brain fitness – a strong combination for heart and mind.⁸ ¹¹
This article is based on carefully researched sources:
Sources & Bibliography
- German Nutrition Society (DGE). "Fat – Functions and Recommendations." (Basic knowledge about fat, absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, heat stability).
- Ohlgart M. "How fatty acids affect your health" - an overview of membrane fluidity, eicosanoids and the omega ratio.
- Avgerinos KI et al. Medium-chain triglycerides induce mild ketosis and may improve cognition in Alzheimer's disease. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;58:101001.
- Fortier M, Castellano CA, Croteau E, et al. A ketogenic drink improves brain energy and some measures of cognition in mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimer's & Dementia. 2019;15(5):625–634. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2018.12.017
- 5a) Estruch R, Ros E, Salas-Salvadó J, et al. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet Supplemented with Extra-Virgin Olive Oil or Nuts. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:e34. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1800389.
5b) Covas MI, Nyyssönen K, Poulsen HE, et al. (EUROLIVE). The effect of polyphenols in olive oil on heart disease risk factors: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2006;145(5):333–341. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-145-5-200609050-00006
5c) Guasch-Ferré M, Li Y, Willett WC, et al. Olive oil consumption and all-cause and cause-specific mortality in US adults. - Conquer JA, Holub BJ. Supplementation with an algae source of docosahexaenoic acid increases (n-3) fatty acids in plasma and erythrocytes of vegetarians. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;71(1):118–124. doi:10.1093/ajcn/71.1.118, Arterburn LM, Hall EB, Oken H. Distribution, interconversion, and dose response of n-3 fatty acids in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;83(6 Suppl):1467S-1476S. doi:10.1093/ajcn/83.6.1467S, EFSA NDA Panel. Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for fats, including saturated fatty acids, polyunsaturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids, trans fatty acids, and cholesterol. EFSA Journal. 2010;8(3):1461. (and supplementary statements 2012) doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1461
- 7a) Estruch R, Ros E, Salas-Salvadó J, et al. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet Supplemented with Extra-Virgin Olive Oil or Nuts. New England Journal of Medicine. 2013;368(14):1279-1290. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1200303. (PREDIMED main publication; shows fewer cardiovascular events with an EVOO-rich diet.)
7b) Guasch-Ferré M, Li J, Hu FB, et al. Olive Oil Consumption and Mortality in US Adults. Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC). 2022;79(2):101-112. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2021.10.041. (Prospective US cohorts; higher olive oil intake associated with lower overall and cardiovascular mortality.) - 8a) Conquer JA, Holub BJ. Alteration of documented (n-3) fatty acid status in vegetarians by the administration of an algal-derived DHA. Journal of Nutrition. 1996;126(12):3032-3039. PMID: 9001371.
8b) Arterburn LM, Oken HA, Bailey-Hall E, et al. Algal-oil capsules and cooked salmon: nutritionally equivalent sources of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Journal of the American Dietetic Association. 2008;108(7):1204-1209. doi:10.1016/j.jada.2008.04.022.
8c) Schmitt D, Tran N, Peach J, et al. Toxicological evaluation of DHA-rich algal oil: genotoxicity, subchronic and developmental toxicity studies. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology. 2012;62(3):449-464. - 9a) Henderson ST, Vogel JL, Barr LJ, Garvin F, Jones JJ, Costantini LC. Study of the Ketogenic Agent AC-1202 in Mild to Moderate Alzheimer's Disease: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter Trial. Nutrition & Metabolism (London). 2009;6:31. doi:10.1186/1743-7075-6-31.
9b) Ota M, Matsuo J, Ishida I, et al. Effects of a Medium-Chain Triglyceride-Based Ketogenic Formula on Cognitive Function in Patients with Mild-to-Moderate Alzheimer's Disease. Neuroscience Letters. 2019;690:232-236. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2018.10.048. (MCT formulation improves selected cognitive domains in AD.)
9c) Lin YN, Tsai CL. The Ketogenic Effect of Medium-Chain Triacylglycerides—A Critical Review. Nutrients. 2021;13(9):3086. doi:10.3390/nu13093086. - Sarter B, Kelsey KS, Schwartz TA, Harris WS. Blood docosahexaenoic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid in vegans: Associations with age and gender and effects of an algal-derived omega-3 fatty acid supplement. Clinical Nutrition. 2015;34(2):212–218. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1461
- Guasch-Ferré M et al. Olive Oil Intake and Mortality. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;79(2):101–112 (associated reduction in overall/cardiovascular mortality).
- 12a) – Hemp oil (overview, cardiovascular/vessel-relevant):
Rodríguez-Leyva D, Pierce GN. The cardiac and haemostatic effects of dietary hempseed and hempseed oil in animals and humans: A review. Nutrition & Metabolism. 2010;7:32. DOI: 10.1186/1743-7075-7-32. PMID: 20409317.
12b) – Walnut oil/walnuts (endothelial function, RCT):
Ros E, Núñez I, Pérez-Heras A, Serra M, Gilabert R, Casals E, Deulofeu R. A walnut diet improves endothelial function in hypercholesterolemic subjects: a randomized crossover trial. Circulation. 2004;109(13):1609-1614. DOI: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000124477.91474.FF. PMID: 15051604. - Data on linseed oil/ALA: ALA content, storage/sensitivity, use in cold cuisine.
13a) – ALA & Cardiovascular Risk (Meta-Analysis):
Pan A, Chen M, Chowdhury R, Wu JHY, Sun Q, Campos H, Mozaffarian D, Hu FB. Alpha-linolenic acid and risk of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;96(6):1262-1273. DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.112.044040. PMID: 23134824.
13b) – ALA conversion to EPA/DHA (controlled diet study):
Goyens PLL, Spilker ME, Zock PL, Katan MB, Mensink RP. Conversion of α-linolenic acid in humans is influenced by the absolute amounts of α-linolenic acid and linoleic acid in the diet and not by their ratio.