Themen dieses Blogartikels:
Table of contents
- What is the cell membrane?
- Structure of the cell membrane – stability meets flexibility
- Stability vs. Fluidity
- Phospholipids explained simply
- Functions of the cell membrane – tasks with a direct influence on your well-being
- Cell-cell interactions – communication at the cellular level
- Lipid rafts and their role – microdomains of the membrane
- Cell membrane & environment – adaptation & protection
- Cell membrane & diseases – when the barrier fails
- Cell membrane & age – the influence of time
- What damages the cell membrane?
- What signals indicate a disrupted cell membrane?
- Nutrients & protective substances for strong cell membranes
- Lifestyle quickies – how to support your cell membranes daily
- Sources & Bibliography
What is the cell membrane?
Every living cell in the body is surrounded by a cell membrane . This membrane separates the cell's contents (cytoplasm) from the outside world, maintains a stable internal environment, and enables targeted exchange of substances¹. It can be thought of as a highly selective border control: nutrients, ions, and water are allowed in, while waste products are allowed out – but only when special "doors" (transport proteins) open. At the same time, receptors are located on the membrane that receive hormones, neurotransmitters, or immune signals and transmit them into the cell. The cell membrane is thus both a barrier and a communication center .
Structure of the cell membrane – stability meets flexibility
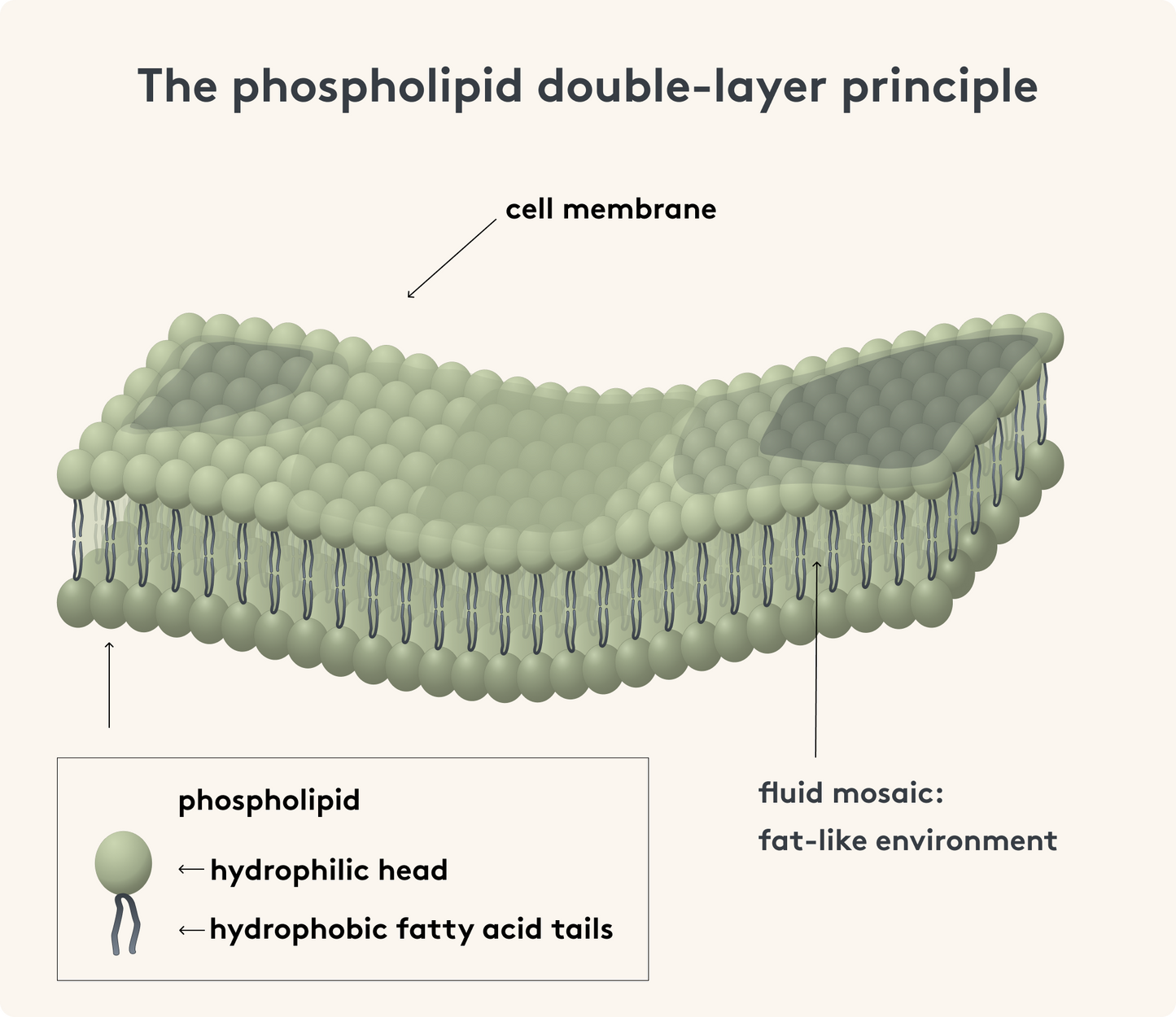
The phospholipid bilayer principle
The basic structure of all cell membranes is a bilayer of phospholipids ².
A phospholipid consists of
- a hydrophilic head (attracts water) and
- two hydrophobic fatty acid tails ( avoid water).
When phospholipids are in an aqueous environment (blood, cell fluid), they automatically align so that their tails point toward each other and their heads point outward. This creates two layers – the lipid bilayer .
Between the lipid tails, a viscous, fat-like environment exists in which proteins can move laterally. This "fluid mosaic" makes the membrane flexible.

Stability vs. Fluidity
In every cell membrane, the ratio of strength and mobility must be right:
- Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds and are perfectly straight. They pack tightly together and strengthen the membrane.
- Unsaturated fatty acids (mono- or polyunsaturated) contain one or more double bonds. They have kinks, creating more "space"—the membrane remains flexible ³.
Cholesterol acts as a “membrane modulator” – in warm conditions it stabilizes, in cold conditions it prevents rigid clumping.
Phospholipids explained simply
Phospholipids are amphiphilic : The water-soluble head interacts with blood or cellular fluid, while the fat-soluble tails hold the bilayer together. This dual nature allows phospholipids to "manage" both water- and fat-soluble molecules ⁴.
Functions of the cell membrane – tasks with a direct influence on your well-being
When the cell membrane fulfills its functions, cellular metabolism runs smoothly.⁵ If it is damaged, this balance is disrupted.
| Core function | Short description | Well-being benefits |
| Selective filter | Regulates which substances enter or leave the cell | Optimal nutrient supply, detoxification |
| Signal platform | Receptors receive hormones, nerve impulses, immune signals | Balance of hormonal system, mood, immune system |
| Energy hotspot | Mitochondrial membranes house the respiratory chain (ATP production) | lasting physical & mental energy |
| Protection from stress | Intact lipid layers neutralize free radicals | Cell protection, anti-aging |
| Cell ID & Communication | External carbohydrate structures give immune cells “ID” | fewer false reactions, better wound healing |
| Oil | Main fatty acids | Membrane benefits |
| Extra virgin olive oil | Oleic acid + lipophilic polyphenols | Protects lipids from oxidation¹⁵ |
| Linseed oil | ALA (vegetable Ω-3) | Precursor for EPA/DHA |
| Rapeseed & walnut oil | moderate Ω-6 / Ω-3 | Good everyday oil |
| Algae or krill oil | EPA/DHA an Phospholipide | Fast storage in membrane |